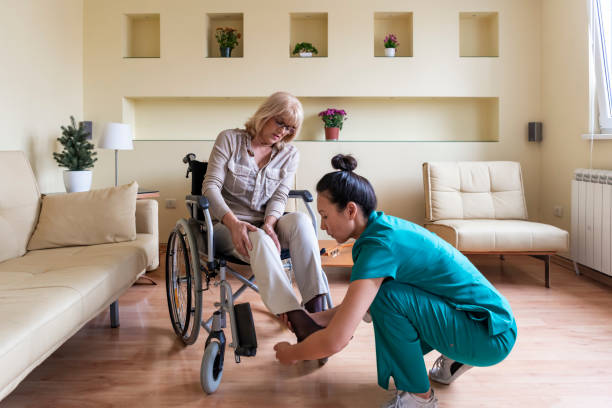
Physiotherapy Assistant
A Physiotherapy Assistant is a crucial healthcare support professional who works under the supervision of licensed physiotherapists to help patients recover from injuries, manage chronic conditions, and improve mobility and physical function. They assist in implementing treatment plans, providing hands-on support, and ensuring patient comfort during therapy sessions. This detailed guide provides the latest information (based on trends up to the most recent data, projected to the current year of 2025) on job roles, education, salary, and prospects within India for this vocational career, with a focus on both government and private sectors.
Job Description
a) Clinical Support Responsibilities:
- Assist physiotherapists in delivering treatment plans, including exercises, stretches, and manual therapy techniques for patients with musculoskeletal, neurological, or respiratory conditions.
- Help patients with mobility aids such as crutches, walkers, or wheelchairs, ensuring proper usage and safety during therapy sessions.
- Prepare treatment areas by setting up equipment like ultrasound machines, electrical stimulation devices, or exercise tools, and ensure cleanliness and sterilization after use.
- Monitor patients during therapy sessions, observing their responses to exercises or treatments and reporting progress or concerns to the supervising physiotherapist.
- Provide basic patient education on exercises or postures to follow at home, reinforcing instructions given by the physiotherapist.
b) Administrative and Support Responsibilities:
- Maintain patient records, documenting therapy sessions, progress notes, and attendance under the guidance of the physiotherapist.
- Schedule appointments for patients, manage follow-up visits, and coordinate with other healthcare staff for integrated care.
- Assist in inventory management by ensuring availability of therapy supplies, such as resistance bands, hot/cold packs, and other materials.
- Support in maintaining a safe and organized therapy environment, adhering to infection control protocols and safety guidelines.
- Handle basic clerical tasks, such as answering patient queries, managing files, and assisting with billing or insurance documentation when required.
Educational Requirements and Study Routes
Eligibility Criteria
| Level | Eligibility |
| Entry-Level (Diploma/Certificate) | High school diploma or equivalent (10+2), preferably with science subjects (Biology, Chemistry, Physics); minimum 50% marks in most cases. |
| Bachelor’s Degree (Optional) | Completion of high school (10+2) with strong grades in science for related undergraduate programs. |
| Advanced Roles (Further Training) | Diploma or certificate in Physiotherapy Assistance; relevant work experience may be preferred for competitive or senior assistant roles. |
Study Routes
| Route | Focus Area | Duration | Outcome |
| Certificate Programs | Physiotherapy Assistance | 6 months to 1 year | Entry-level physiotherapy assistant roles in hospitals, clinics, or rehabilitation centers. |
| Diploma Programs | Physiotherapy Technology / Assistance | 1-2 years | Broader scope for assistant positions in government and private sectors. |
| Bachelor’s Degree (Optional) |
| 3-4 years | Pathway to advanced assistant roles or preparation for full physiotherapy licensure with further studies. |
| Short-Term Training (Optional) | Rehabilitation Support, Basic Manual Therapy | 3-6 months | Specialized skills for patient handling or therapy support; often for skill enhancement. |
Entrance Tests (India):
- National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET): Required for some undergraduate physiotherapy-related courses in certain institutions, though often not mandatory for assistant-level diploma or certificate programs.
- University-Specific Entrance Exams: For diploma or related degree programs in physiotherapy assistance (e.g., AIIMS Paramedical Entrance Exam, JIPMER Entrance Exam).
- State-Level Entrance Tests: Conducted for physiotherapy assistant courses in various states, such as Tamil Nadu Common Entrance Test (TANCET) or Maharashtra Common Entrance Test (MHT-CET).
- Direct Admissions: Many private institutes and vocational training centers offer merit-based admissions based on 10+2 marks for certificate and diploma courses.
Skills and Competencies
- Technical Skills: Basic knowledge of physiotherapy techniques, use of therapy equipment, and patient handling methods under supervision.
- Physical Skills: Stamina and strength to assist patients with mobility, support during exercises, and handle equipment for prolonged periods.
- Analytical Skills: Attention to detail in observing patient progress and reporting accurately to the supervising physiotherapist.
- Soft Skills: Empathy and patience in dealing with patients experiencing pain or mobility issues; effective communication for providing instructions and reassurance.
- Safety Awareness: Understanding of infection control, patient safety protocols, and compliance with guidelines from Indian regulatory bodies like the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Adaptability: Ability to work with diverse patient groups (e.g., elderly, children, athletes) and adjust to varying treatment plans or workloads.
Work Environment
a) Clinical Settings:
- Government Sector: Roles in public hospitals, rehabilitation centers, and primary health centers (PHCs); often involves working with underserved communities and may include shift work.
- Private Sector: Positions in private hospitals, physiotherapy clinics, and sports rehabilitation centers; may offer better infrastructure but sometimes demand longer hours.
b) Community and Specialized Settings:
- Government Sector: Work in community health programs or government-funded rehabilitation initiatives focusing on disability support or geriatric care.
- Private Sector: Roles in home care services, fitness centers, or corporate wellness programs; often tied to personalized patient care or preventive therapy.
Salary Structure (Tentative as of Recent Data in India, Projected to 2025)
Physiotherapy Assistant (Clinical and Community Settings)
| Level | Government Sector (INR Annual) | Private Sector (INR Annual) |
| Entry-Level | ₹1,80,000 - ₹2,50,000 (Pay Scale: Level 2-3 under 7th CPC) | ₹2,00,000 - ₹3,00,000 |
| Mid-Level | ₹2,80,000 - ₹4,00,000 (Pay Scale: Level 4-5) | ₹3,20,000 - ₹4,50,000 |
| Senior-Level | ₹4,50,000 - ₹5,50,000 (Pay Scale: Level 6-7) | ₹5,00,000 - ₹6,50,000 |
Note: Salaries vary based on location (urban vs. rural), experience, and specific employer. Government sector salaries often follow the 7th Central Pay Commission (CPC) scales and include benefits like Dearness Allowance (DA), House Rent Allowance (HRA), pensions, and job security. Private sector roles may offer higher initial pay, bonuses, or incentives but often lack long-term stability or comprehensive benefits. Data is approximate and subject to change based on economic conditions and policy updates in 2025.
Job Outlook in India
- Clinical Physiotherapy Assistant: High demand driven by the increasing prevalence of lifestyle-related conditions (e.g., back pain, arthritis), aging population, and post-surgical rehabilitation needs under schemes like Ayushman Bharat.
- Community and Specialized Roles: Growing need in disability support, geriatric care, and sports injury rehabilitation, especially with rising awareness of physical fitness.
- Emerging Areas: Increased focus on home-based physiotherapy services and telemedicine support for remote therapy guidance; growth in corporate wellness programs requiring physiotherapy assistance.
Top Institutes for Relevant Studies in India
| Institute | Program Focus | Location | Sector Affiliation |
| All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) | Physiotherapy Assistance | New Delhi | Government |
| Christian Medical College (CMC) | Physiotherapy Support, Rehabilitation Training | Vellore, Tamil Nadu | Private |
| Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & Research (JIPMER) | Physiotherapy Courses | Puducherry | Government |
| Manipal Academy of Higher Education | Physiotherapy Assistance, Rehabilitation Science | Manipal, Karnataka | Private |
| University of Delhi | Rehabilitation Support | Delhi | Government |
| Banaras Hindu University (BHU) | Physiotherapy Technology | Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh | Government |
| Amity University | Physiotherapy Assistance, Rehabilitation Studies | Noida, Uttar Pradesh | Private |
| SRM Institute of Science and Technology | Physiotherapy Support, Rehabilitation Technology | Chennai, Tamil Nadu | Private |
| Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) | Physiotherapy Assistance | Chandigarh | Government |
| Lovely Professional University (LPU) | Physiotherapy Assistance, Rehabilitation Support | Jalandhar, Punjab | Private |
Note: Admission requirements vary; government institutes often have lower fees but higher competition through entrance exams, while private institutes may have higher fees with more flexible admission processes. Check specific institute websites for entrance tests, eligibility, and application processes.
Career Advancement in India
a) Clinical Path:
- Government Sector: Progress to roles like Senior Physiotherapy Assistant or Rehabilitation Technician Assistant with experience; promotions based on seniority and exams under state/central service rules.
- Private Sector: Move to specialized assistant roles in areas like sports therapy or pediatric rehabilitation with additional certifications or training.
b) Further Education Path:
Government and Private Sector: Pursue advanced studies (e.g., Bachelor of Physiotherapy - BPT) to become a licensed physiotherapist after gaining experience as an assistant, opening pathways to independent practice or supervisory roles.
Pros and Cons of the Profession
| Pros | Cons |
| Direct impact on patient recovery through hands-on support in therapy sessions | Physically demanding role requiring stamina to assist patients and handle equipment for long hours |
| Contribution to improving quality of life for patients with mobility or pain issues | Exposure to emotional stress when working with patients in chronic pain or with severe disabilities |
| Diverse work settings ranging from hospitals to community programs and home care | Limited decision-making authority; must work under strict supervision of physiotherapists |
| Job security, pensions, and additional benefits in government sector roles, providing stability | Private sector roles may involve irregular hours or lack of long-term benefits compared to government positions |
| Opportunities for societal impact through rehabilitation programs and public health initiatives | Continuous learning required to stay updated with new therapy techniques or equipment usage |
Emerging Trends in India (Current Perspective, 2025)
- Technology: Adoption of wearable devices and tele-rehabilitation platforms for remote therapy support; use of mobile apps for patient exercise tracking.
- Public Health Focus: Government emphasis on rehabilitation services through schemes like the National Health Mission (NHM), creating demand for physiotherapy assistants.
- Aging Population and Lifestyle Issues: Rising need for physiotherapy support due to geriatric care requirements and lifestyle-related conditions like obesity or sedentary habits.
- Skill Development: Government policies like Skill India and the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) offer training and certification opportunities for physiotherapy assistants.
How to Get Started in India
- Education: Choose a relevant program (Certificate/Diploma) based on career goals from recognized Indian institutes, considering government (lower cost, competitive) or private (higher cost, easier access) institutions.
- Certifications: Obtain credentials through bodies like the Indian Association of Physiotherapists (IAP) or state-level councils for physiotherapy support roles; pursue short-term courses in rehabilitation or patient care.
- Internships: Gain hands-on experience in government hospitals (through schemes like NHM), private physiotherapy clinics, or rehabilitation centers.
- Networking: Join associations like the Indian Association of Physiotherapists (IAP) for opportunities, workshops, and professional development.
- Government Job Applications: Prepare for recruitment exams conducted by bodies like the Staff Selection Commission (SSC) or state public service commissions for roles in public healthcare facilities.
- Private Sector Opportunities: Apply to hospitals, clinics, or rehabilitation centers through job portals like Naukri.com, LinkedIn, or direct company websites.
- Stay Updated: Follow advancements via Indian journals (e.g., Indian Journal of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy), webinars, and conferences focused on rehabilitation and healthcare.
Key Employers in India
| Sector | Category | Employers |
| Government Sector | Clinical Settings | Public hospitals under state health departments, AIIMS, Primary Health Centers (PHCs), National Health Mission (NHM) |
| Community Settings | Government rehabilitation centers, disability support programs under Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment | |
| Private Sector | Clinical Settings | Private hospitals like Apollo, Fortis, Max Healthcare, physiotherapy clinics |
| Specialized Settings | Sports rehabilitation centers, home care services, corporate wellness programs |
Challenges Specific to India
- Resource Constraints: Government facilities, especially in rural areas, may lack modern therapy equipment or adequate staffing, leading to workload stress for assistants.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to guidelines from bodies like the Ministry of Health or state councils requires meticulous attention to patient care protocols.
- Regional Disparities: Opportunities and infrastructure vary widely between urban centers (e.g., Delhi, Mumbai) and rural areas, affecting job conditions and pay.
- Public Awareness: Limited understanding of physiotherapy benefits in some communities can lead to challenges in patient compliance or demand for services.
A career as a Physiotherapy Assistant in India offers a rewarding opportunity to support patient recovery and improve quality of life, with diverse roles in both government and private sectors. Supported by national health initiatives and growing awareness of rehabilitation needs, this vocational path is promising for those interested in healthcare support. With structured education, certifications, practical experience, and adaptability to evolving trends, individuals can build stable careers while contributing to public health and wellness in India.
Leading Professions
View AllCAREER VIDEOS
Interested? Take the next step for this career
Skills Needed

This page includes information from O*NET Resource Center by the U.S. Department of Labor, Employment and Training Administration (USDOL/ETA). Used under the CC BY 4.0 license. O*NET® is a trademark of USDOL/ETA.
© 2025 TopTeen. All rights reserved.